Red Hat CRC is intended to be run on a laptop locally. That includes the web access to the UI. For a local lab setup where a separate computer is used to run software, this is not the best usage scenario. Good news is that it is possible and you can find some official information about the setup:
https://www.openshift.com/blog/accessing-codeready-containers-on-a-remote-server/ 🔗
https://gist.github.com/tmckayus/8e843f90c44ac841d0673434c7de0c6a 🔗
Configure firewall
sudo yum install policycoreutils-python-utils
Configure the firewall.
sudo systemctl start firewalld
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=80/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=6443/tcp --permanent
sudo firewall-cmd --add-port=443/tcp --permanent
sudo systemctl restart firewalld
sudo semanage port -a -t http_port_t -p tcp 6443
Without the firewall confige and more importantly, semanage, haproxy won’t be able to listen on port 6443.
Install haproxy
sudo yum install haproxy
Haproxy config
For the configuration the IP address of the server is needed. Once for the server, and once for the CRC instance. Both can be obtained in CentOS via ifconfig
ifconfig
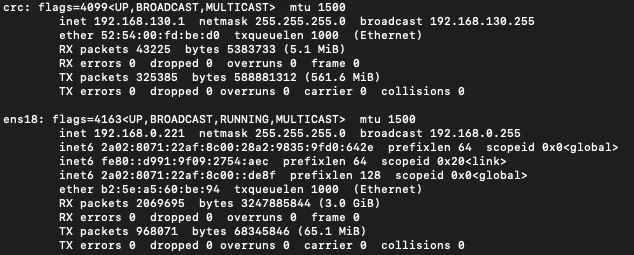
- CRC: 192.168.130.11
- Server: 192.168.0.221
Edit the haproxy config file at /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
Insert the following content (for both crc and server IP address as provided above).
global
log /dev/log local0
defaults
balance roundrobin
log global
maxconn 100
mode tcp
timeout connect 5s
timeout client 500s
timeout server 500s
listen apps
bind 0.0.0.0:80
server crcvm 192.168.130.11:80 check
listen apps_ssl
bind 0.0.0.0:443
server crcvm 192.168.130.11:443 check
listen api
bind 0.0.0.0:6443
server crcvm 192.168.130.11:6443 check
Start haproxy
The haproxy configuration makes haproxy forward requests to crc an port 6443. OpenShift must be up and running for haproxy to connect to it and start up without errors.
sudo systemctl start haproxy
In case starting haproxy is not working, check the log via:
sudo journalctl -xe
Fix the error mentioned in the output and then try to start haproxy again.
Client machine
The client machine is the remote laptop from which the user will connect to OpenShift. As CRC is using some internal DNS names and normally sets them in the local hosts file, these need to be added on the client machine. As IP, use the IP address of your server that runs CRC.
vim /etc/hosts
192.168.0.221 api.crc.testing console-openshift-console.apps-crc.testing default-route-openshift-image-registry.apps-crc.testing oauth-openshift.apps-crc.testing
Remember: for each route / app deployed on OpenShift, a new entry must be added to the above host entry.
Access
On the client machine / laptop, open a browser and navigate to the OpenShift web ui.
https://console-openshift-console.apps-crc.testing/ 🔗