Red Hat CodeReady Containers 🔗 allows to run a local OpenShift 4 environment locally on a Laptop. While it can be installed on a wide range of systems, one of the better choices is Red Hat Linux or a similar system like CentOS.
Hint
Make sure to have enough RAM and storage available or when in an VM, assigned. When choosing automatic partitioning, you might end up with not enough disk space for /home to run CRC. In that case, you’ll have to install CRC to some path in the root (/) partition.
Preparations
Check if some preparations need to be done, like installing any host agent if CentOS is running in a virtualization platform like Proxmox. In that case, install the host agent 🔗.
yum install qemu-guest-agent
systemctl enable qemu-guest-agent
systemctl start qemu-guest-agent
Installing vim might make life easier, so:
yum install vim
Pre-requisites
Network Manager
After installing CentOS install Network Manager. This is a requirement from CRC for handling network.
yum install NetworkManager
Copy CRC installer
Copy and untar/zip the CRC installer. CRC cannot be run as root. Copy the installer to a user directory. When installing CentOS you get asked to add a user, in my case I added a user named tobias.
scp crc-linux-amd64.tar.xz tobias@192.168.0.221:/home/tobias
After the installer is copied to the VM, log on as above user and untar/unzip the file.
tar -xvf crc-linux-amd64.tar.xz
This will give you the file crc. That’s the Eierlegende Wollmilchsau 🔗 for CRC. It is used to install, run, interact, and delete CRC.
Installation
Start the installation by calling the crc program extracted above. Installation is basically two steps: setup to check the pre-requirements and then starting CRC.
Setup
cd crc-linux-1.27.0-amd64
./crc setup
CRC setup will start. The step includes a pre-flight check. If your system contains a known limitation that will stop CRC to work, setup will stop and you’ll have to fix the error. Setup will configure DNS and install a VM that contains OpenShift.

![]()
Start CRC
A working internet connection is needed for CRC to start successfully. Check that DNS resolution works and that dnsmasq and NetworkManager are running and working. It is a good idea to give more RAM and CPU to the OpenShift VM. By default, it is 8 GB RAM which is not enough.
./crc start -m 16384 -c 4
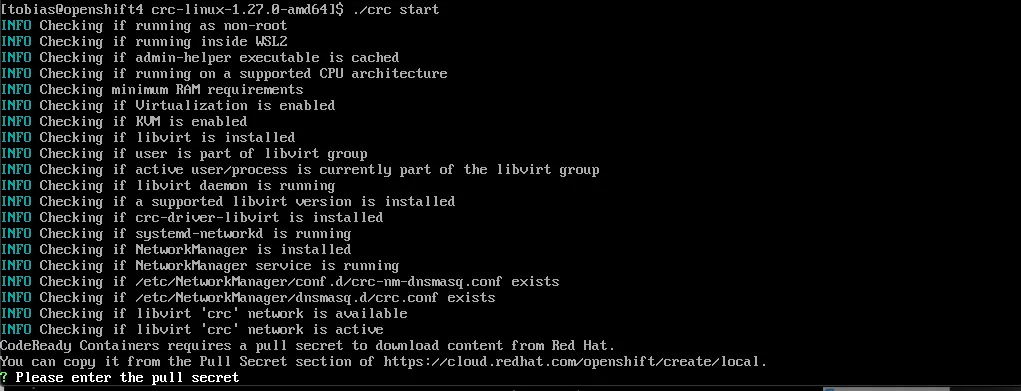
Paste the pull secret. As an alternative, you can provide the pull secret file to the start command.
./crc start -m 16384 -c 4 -p /home/tobias/pull-secret.txt
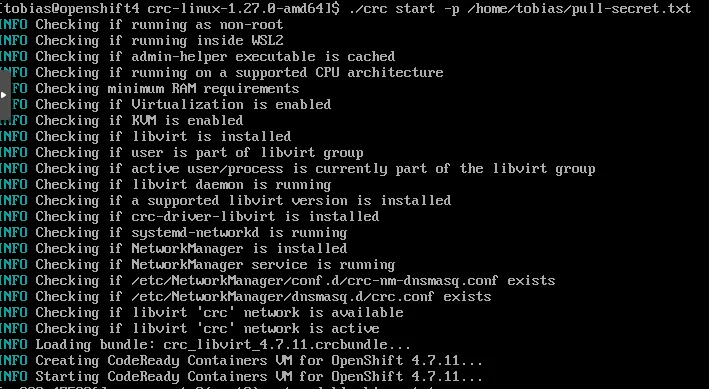
Starting CRC will take a while. After all operators are started and a self-check confirms that OpenShift is ready to be used, some commands needed to interact with OpenShift are shown.
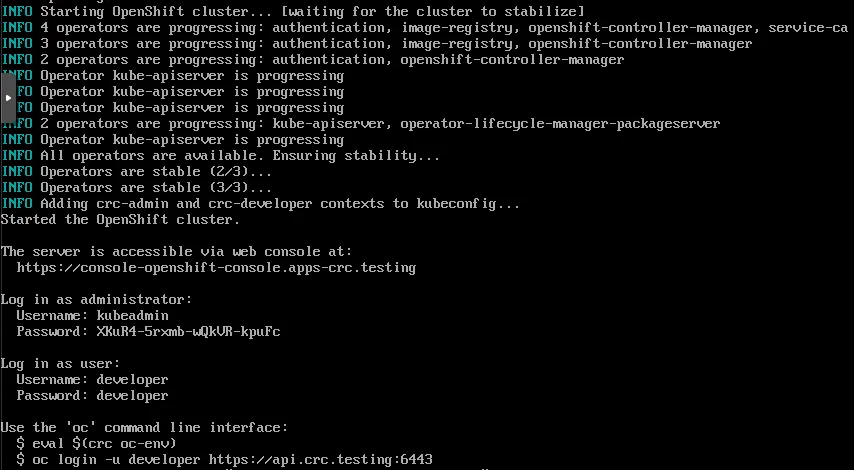
That’s it. CRC started and OpenShift4 is running in the provided VM. OpenShift is ready to be used.
Validation
The base validation is to set up oc as a command and to log on either as developer or kubeadmin. This must work!
eval $(./crc oc-env)
oc login -u developer https://api.crc.testing:6443
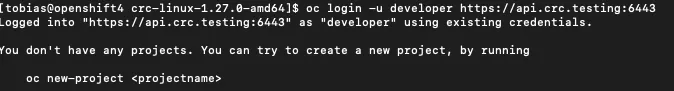
As a next validation step, check the status of CRC.
./crc status
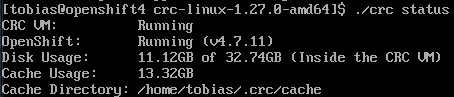
Starting crc will set up the hosts file to include the DNS names for the OpenShift 4 services.
more /etc/hosts
192.168.130.11 api.crc.testing canary-openshift-ingress-canary.apps-crc.testing console-openshift-console.apps-crc.testing default-route-openshift-image-registry.apps-crc.testing downloads-openshift-console.apps-crc.testing oauth-openshift.apps-crc.testing
