OpenSSL CA to sign CSR with SHA256 – Create CA
The overall process is:
- Create CA
- Private CA key
- Create private key
- Check private key
- Public CA certificate
- Create public certificate
- Check public certificate
- Private CA key
- Sign CSR
- SHA-1
- Create CSR using SHA-1
- Check CSR
- Sign CSR enforcing SHA-256
- Check signed certificate
- SHA-256
- Create CSR using SHA-256
- Check CSR
- Sign CSR
- Check signed certificate
- SHA-1
Create a CA
To have a private CA with openssl, at least two steps are need: you need to create a private key and a public certificate. The public certificate will be used to sign CSRs.
Private CA key
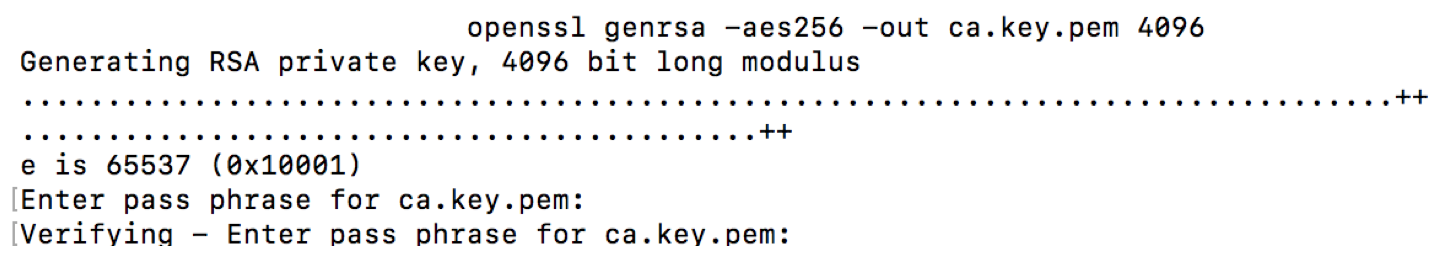
Create private key
openssl genrsa -aes256 -out ca.key.pem 4096
The command will generate a private key using random data and ask you to provide a pass phrase. While possible to enter an empty pass phrase, it is highly recommended to provide one. In my test case, I simply use “test”. Remember: it is not a password, but a phrase. If you want, go crazy and use a full sentence.
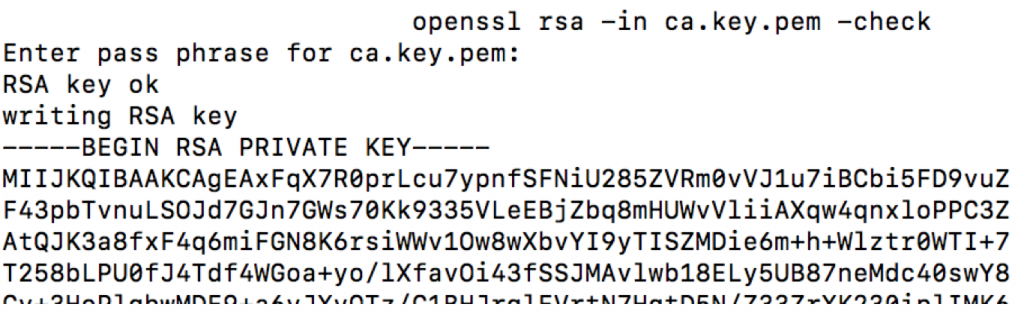
Check private key
This creates a pass phrase protected private key. The key is password protected. This can easily be seen by opening the key and checking for the —–BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY—– section.
To validate that everything is OK with the private key, openssl can be used
openssl rsa –in ca.key.pem -check
The output prints RSA key ok.
Public CA certificate
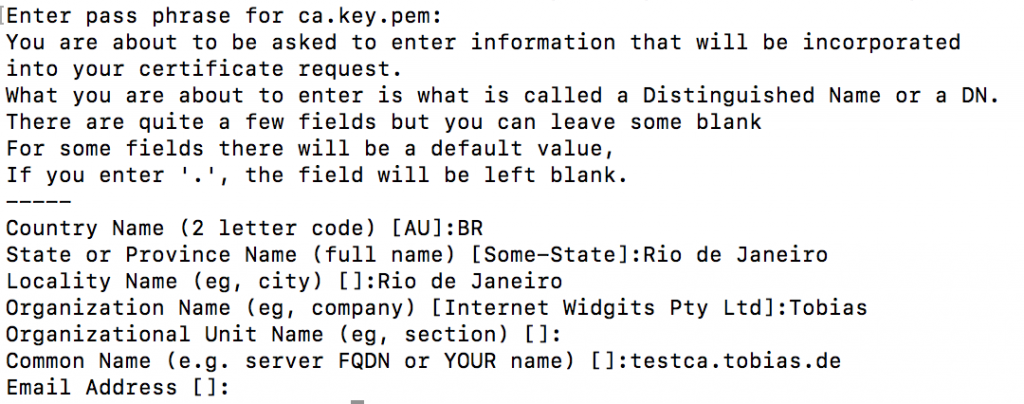
Create public certificate
openssl req -key ca.key.pem -new -x509 -days 5000 -sha256 -extensions v3_ca -out ca.cert.pem
You`ll need to inform the pass phrase of the private key as well as some additional administrational data like the location of the server.
This created a new certificate for the CA using the private key.
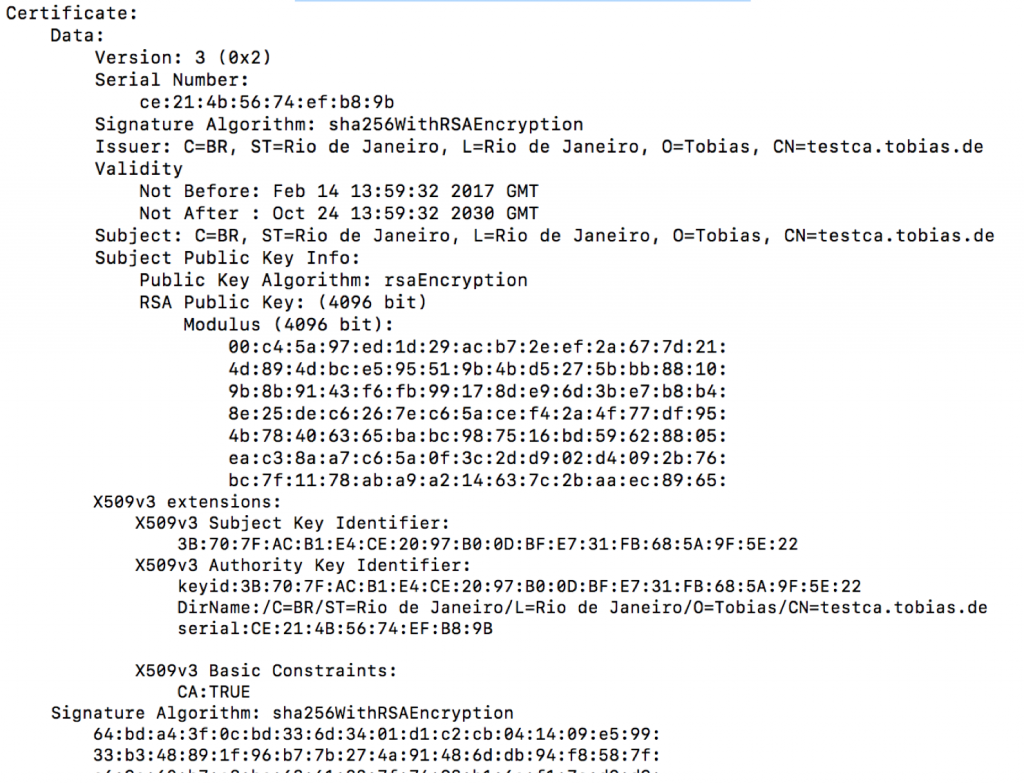
Check public certificate
openssl x509 -in ca.cert.pem -text -noout
The Signature Algoritm is using SHA-256.
Using the above two commands, a private key and public certificate with usage type for CA was created. This certificate can now be used to sign CSR requests.


0 Comments